Can You Use Art Made by Following a Tutorial in a Commercial Product
Lesson 3: Copyright and Fair Use
/en/useinformationcorrectly/avoiding-plagiarism/content/
Copyright and fair utilize
In our Avoiding Plagiarism lesson, nosotros gave y'all tips for citing, quoting, and incorporating various sources into your writing projects. However, depending on what types of sources you use, you may also have to consider copyright and off-white employ laws. For example, if you lot want to utilize someone else's photo or song in one of your own projects, yous'll demand to brand certain you have the legal right to practise and so.
In this tutorial, you'll learn virtually the copyright protections that apply to work posted online, including images, text, videos, and more than. You'll also larn about the rules that determine which of these resources you can use, and how you lot tin use them.
Watch the video beneath to learn about copyright, public domain, and fair use.
The laws discussed in this tutorial are U.s.a. laws. No lawyer was involved in preparing this tutorial. We are not legal experts, and this tutorial should not exist taken as legal advice.
What is copyright?
Copyright is the legal concept that works—art, writing, images, music, and more—belong to the people who create them. Co-ordinate to copyright police force, any original content y'all create and record in a lasting form is your own intellectual holding. This means other people can't legally copy your work and pretend it's their own. They can't make money from the things you create either.
You can still cite and refer to other sources (including copyrighted materials) in your piece of work. But to use, copy, or modify a copyrighted work, you need permission from the person who holds the copyright. This permission is called a license.
Although everyone has the right to crave that others respect their copyright and ask permission to use their piece of work, some people and organizations choose to license their content more freely. They do this by giving their piece of work a Creative Commons license, or by placing their work in the public domain.
Review the infographic to get an overview of the differences amid traditional copyright, Creative Commons, and public domain.

Obtaining complimentary content
If everything on the Internet belongs to someone, how do you obtain images, music, and other materials you tin use in your projects for free? The answer is through public domain and Creative Commons-licensed content. To learn more, review the tips beneath.
Tip #1: Employ public domain content
There are no restrictions on using works that are in the public domain, which means you can utilize them however yous want—short of claiming that you created them yourself. Unfortunately, it's not always easy to tell whether or non something is in the public domain. There may exist some cases when yous know for sure that a work is public domain (for instance, if you find a photo or text you are sure was published earlier 1923), simply for the most part the best way to discover public domain content is to search for information technology specifically.
For help finding public domain content, visit these resource:
- Prelinger Archives
- U.Southward. Authorities Photos and Images
Tip #ii: Use Artistic Commons content
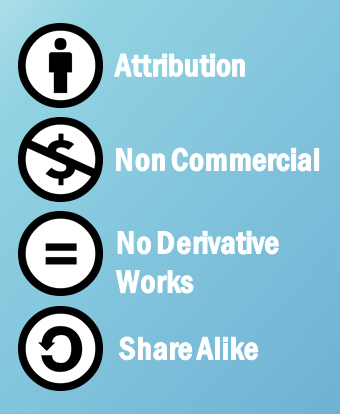 The symbols for Creative Commons licenses
The symbols for Creative Commons licenses
Although Creative Eatables content won't price you whatever coin to obtain, it's not totally costless: To use information technology, you must follow certain rules. People who choose to brand their content Creative Eatables tin can choose one or more of these licenses to use to their work:
- Attribution: You must credit the creator in order to use, copy, or share the content.
- Not-Commercial: You can't make a turn a profit from the content.
- No Derivative Works: You can't alter the content.
- Share Alike: Yous can modify the content, but you lot accept to let other people utilize your new work with the same license as the original. You can't care for any Share Alike work that y'all adapt as your ain copyright, even if you radically alter it.
For help finding Creative Commons content, try these resources:
- Wikimedia Commons
- Flickr: Creative Commons
- Creative Commons Search
How to tell if content is Creative Commons
To tell if a piece of content is Creative Eatables, look for the Creative Commons symbol, equally well as symbols that indicate exactly which licenses apply to it.

For instance, the symbols in the instance below indicate that the photograph has three licenses: Attribution, Non Commercial, and No Derivative Works. This means you can use this photo if you credit the person who created it, don't make money from it, and don't change it.
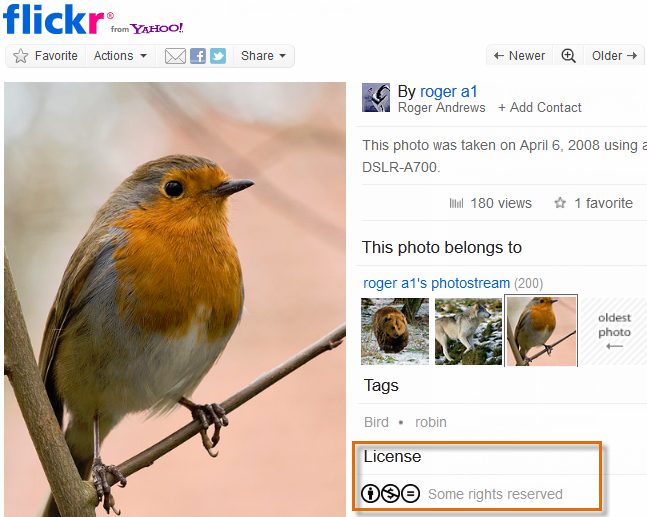 Creative Commons license information for a photo
Creative Commons license information for a photo
Finding content with Google
Google allows you to filter your search results to just show Creative Commons and public domain works. When conducting an avant-garde search, you can choose which usage rights you lot desire Google to search for. For case, if you lot're searching for an image to use in your web log, you lot can change the usage rights to free to use or share.
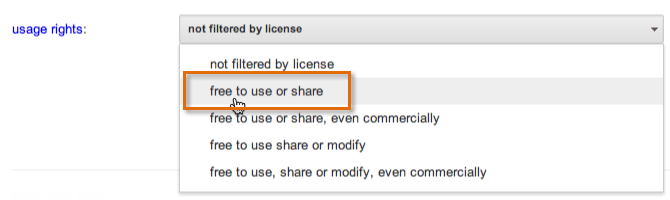 Filtering a Google search by usage rights
Filtering a Google search by usage rights
For more information on conducting an advanced search, review the Advanced Search Strategies portion of our Google Search Tips lesson.
Using copyrighted material

As you learned before, you generally need to license copyrighted fabric in gild to use information technology, which ofttimes costs money. The exception to this is a rule called fair use. Fair employ means y'all tin can use copyrighted textile without a license only for certain purposes. These include:
- Commentary
- Criticism
- Reporting
- Enquiry
- Teaching
You can't but grab a copyrighted photo and utilize it on your web log because you think it'due south pretty. Withal, information technology probably would exist considered fair use if you included the photo in a weblog postal service that commented on and analyzed the lensman's piece of work.
Guidelines for fair use:
- A bulk of the content you create must be your ain.
To render to the case above, information technology's probably fair use to include a few relevant photos to back up your ideas in a web log post, presentation, or research paper. However, using these aforementioned photos in a project with only a few lines of commentary might not be off-white use. Every bit some other instance, let'south imagine you found a useful tutorial you wanted to feature on your web log. Including ane tip from the tutorial would be fair utilise. Just republishing the entire tutorial would not be fair use, fifty-fifty if you linked to the original source. - Give credit to the copyright holder.
In society for something to be fair apply, you must requite total credit to the person who created it. This includes the creator's name, as well as other information that will help people detect the original work or source. For example, if you adjust a recipe that was originally published on a cooking website, you lot should include a link to the original page. For more than help citing your sources, review Avoiding Plagiarism. - Don't make money off of the copyrighted piece of work.
In general, it'due south much easier to claim fair employ when you lot're using the copyrighted cloth for noncommercial purposes. While posting images of your favorite Telly shows and adding funny captions and commentary might be considered fair utilize, selling these images on T-shirts would not.
Misusing copyrighted cloth
The concept of fair use can be tricky, specially when it comes to creating work you don't intend to post or publish. For example, if y'all download a series of graphics from a designer's website and utilise them to create a PowerPoint template for you and your coworkers (without permission), y'all could argue that it was never meant for the public and that you didn't mean whatsoever impairment.
In situations like this, information technology's important to put yourself in the copyright holder'southward shoes. It'southward truthful that he or she will probably never find out about the template. It's also a relatively minor violation because you're just using the graphics around the function.
Merely how would yous feel if you lot were a graphic designer and learned that people were using your work (your livelihood) in a fashion y'all didn't intend? And you're not getting paid or credited for it!
In short, it's better to do what's right than to hazard violating copyright and fair use laws. Even if you lot think what y'all're doing is not a big bargain, the copyright holder may disagree. If someone requests that you lot remove his or her materials from your piece of work, y'all should do so immediately. Otherwise, you can suffer serious consequences, including:
- Having your website shut down if your work is published online—like on a blog—after the copyright holder complains to your hosting service
- Getting sued by the copyright holder
Licensing copyrighted content
If y'all want to use copyrighted content in a way that doesn't fall under off-white use, you lot'll have to license it in lodge to get permission to post it. If you lot're interested in purchasing the rights to apply images, video, and other media in your work, you may want to visit the following stock photo sites:
- iStockphoto
- Photos.com
- Adobe Stock
Sharing copyrighted videos
Video-sharing sites like YouTube and Vimeo offer the option to share videos past embedding them. When you lot embed a video, it automatically creates a link back to the place where it was originally posted. Because the original creator or poster is automatically credited, y'all don't have to worry about going through whatever extra steps to give credit.
Be aware that many videos on these sites—particularly videos of Television shows and movies—are in violation of copyright law, and may be removed from YouTube at any fourth dimension. If a video is removed from YouTube, it will as well be removed from wherever you've embedded it. Yous should never embed a video that you lot know is breaking copyright laws.
 An embedded video from YouTube
An embedded video from YouTube
Protecting your intellectual property
Copyright protects the things you create also. Yous ain the original content you mail service on your web log, share on your website, or write in your inquiry newspaper. If people re-create or steal your intellectual belongings, you take the correct to try and stop them.
Guarding your content online
The all-time style to protect your content is to continue an centre out for information technology elsewhere. These tips can assistance yous determine if someone else has published your work online, like on a website or blog.
- Utilize plagiarism search services.
If you choose to publish your work online, these services will analyze your blog or site, then search for sites with identical content. Copyscape.com is a reputable site with a free plagiarism search. - Fix Google Alerts for excerpts of your work.
Google Alerts is a service y'all can utilize to automatically email you lot when sites post new information virtually a person, matter, or event. You can create alerts for things y'all've written by inbound a few sentences from your work in the Search Query field. (Make sure to use quotation marks.) If that text shows up elsewhere on the Web, you'll receive an e-mail. Setting upward a Google Alert for a blog post
Setting upward a Google Alert for a blog post - Add watermarks to your images.
A watermark is something you add to an paradigm to identify yourself equally its creator—usually a symbol or some text. If you cull to share your images online, watermarks brand it easy for you lot and other people to recognize images you lot created. They also tin can have the upshot of discouraging others from taking your images in the first identify. You can easily create watermarks in image-editing programs like Picasa and Photoshop. A watermarked image
A watermarked image
What to do if you find your content on another site
In that location are two things you tin do if yous find your images, text, or other media on someone else'south website or weblog. First, you can contact the person who runs the blog or site that took your content. Nigh blogs list a contact email address, simply if you can't find ane you can ever exit a comment on the offending post. Ask firmly just politely to remove your content (or give you credit if you don't mind sharing it). This tin can work, especially in cases when the other person didn't realize any wrongdoing had occurred.
If contacting the blogger doesn't work, y'all may want to file a DMCA takedown asking. DMCA refers to the Digital Millenium Copyright Act, a law that'due south designed to help copyright holders protect their content. Under this police, if a site steals your original content you can complain to that site's service provider. If the service provider finds your complaint valid, it will take down the content.
To learn more about filing a DMCA complaint, read How to Transport a DMCA Takedown Discover by Carolyn East. Wright from the blog Blackness Star Rising.
/en/useinformationcorrectly/how-to-copyright-your-content/content/
isabellesilvapinto.blogspot.com
Source: https://edu.gcfglobal.org/en/useinformationcorrectly/copyright-and-fair-use/1/

0 Response to "Can You Use Art Made by Following a Tutorial in a Commercial Product"
Post a Comment